Catla catla, Labeo rohita and Cirrhinus mrigala are the fastest growing and consumer preferred species among Indian major carps. Besides exotic carps viz. Ctenopharyngodon idella and Hypophthalmichthyes molitrix do form an important component of composite culture. These carps do not breed spontaneously in confined water, need hormonal induction for the purpose. Hence, adequate prime brood are essential for commercial seed production. Brood management practices deals mainly with the brood recruitment, pond management and stress management.
RECRUITMENT
Recruitment is a process begin with collection of quality seed as a critical input, for raising and rearing the promising brood for induced breeding. Such critical input may be obtained from riverine collection or from extensive culture system. Seed input from selective breeding process are mostly preferred. However, care is to be taken not to collect any fingerlings from affluent contaminated water, overcrowded intensive carp culture system and pond with any disease outbreak during near past.
POND MANAGEMENT
Management practices play key role in raising and rearing programme. In the process ponds environment are maintained productive and stress free by application of liming fertilizer and feeding rate etc. Pond Management practices do complete in two phases. (A) Brood raising and (B) Brood rearing.
Catalogue of each stock of the breeding farm reflecting the details of gonadal maturation and breeding response is required to be maintained.
Brood Raising Pond Preparation
A suitable brood fish pond varies 0.2 ha to 0.5 ha preferably rectangular in shape and water depth 1.5 m during peak summer. Drainable pond with a provision of water replenishment facilities is most preferred. The pond should be free from aquatic weeds, predators and weed fish. Aquatic weed is to be removed manually and mechanically as far as practicable. Chemical weed control should be avoided to overcome the biological impact on brood fish. Methods adopted for eradication of predatory and weed fishes are by repeated netting, dewatering and application of suitable piscides before stocking, Mahua oil – cake 250 kg/ha or bleaching powder 300 kg/ha (25-30 ppm chlorine level) acts as effective piscides. Quantity of bleaching powder can be reduced to half when it is in combination with urea at 100 kg/ha. Its application should be 24 hours prior to bleaching application.
Stocking.
Yearling are preferably to be collected from different natural resources or from extensive culture system avoiding waste water, industrial affluent and sewage culture system and kept under quarantine condition for 2-3 months. Out of this, healthy and fast growing carps are selected for brood raising programme. Catla, rohu, mrigal, grass carp and silver carp in the ratio 3:2:2:2:1 are stocked @ 1500 kg/ha. Overcrowding and intensive carp culture practices which may invite physiological stress to fish. They are to be fed with formulated diet for proper gonadal development.
Fertilization
Fertilization and liming programme schedule is important to maintain ponds hygiene, pH and optimum plankton (2 ml sediment of plankton in 50 I of water). Plankton free clear water allow the growth of aquatic weeds and algalmat. Quantity of such inputs in brood ponds are subjected to manipulation according to water quality as follows :
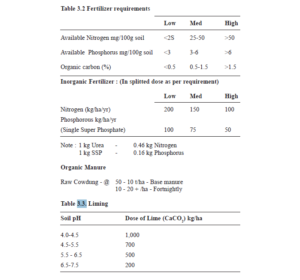
Brood rearing Stocking
The prospective spawners are selected and reared at least 5-6 months ahead < the breeding season. Healthy adults of 2-4 kg and 2 + years of age is reared @ 10C kg/ha following principal species rearing method i.e. 60% dominant species and othei as subsidiaries required for maintenance of brood pond ecosystem. Spent broods < preceeding breeding season are also brought in for the purpose which are termed i professional brood. Such brood are always preferred as the initial stock for multipl breeding programme. This brood certainly spawn 1-2 months early and show bette brooding response as compared to traditional breeders.
Feed for brood rearing
A supplementary protein rich feed is given daily @ 2-3% of the body weight, i the prepatory phase. Brood in maturing phase require reduced diet @ 1-2% of the body weight. Powdered feed is brodcasted in catla dominated pond. Rohu dominate brood stock prefer semi soaked ingredients suspended in the column water in perforated bag whereas application of soaked feed is prescribed in mrigal and grass car rich pond. Silver carp dominated pond needs special attention towards supplementar feed. Regular removal of weed fishes required to avoid competition for food with car brood. The composition of formulated feed is
Formulated feed for Indian Major Carps
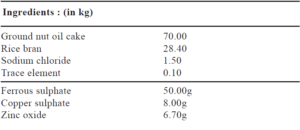
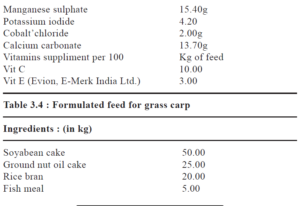
MANAGEMENT OF SPENT BROODS
Spent brood is reared in separate plankton rich pond by following same brood husbandry practices. Broods should be treated at regular interval with pottassium permanganate solution (5 ppm) until they become free from secondary infection. The recovered individual may again incorporated with brood rearing system.
Stress management
During the course of brood rearing breeding stress are needed to be minimised for achieving optirnum production of seed. Some are dealt as follows :
Chemical Stress
Often the brood develops argulosis and the pond are treated with insecticide like malathion and gammexine (BHC) etc. It is observed that treated broods give very poor breeding response and poor quality of gametes. Thus treatment should be done in isolation, not in enmass. The water quality is maintained by following proper fertilization and liming schedule. Some of the optimum physical and physico-chemical parameters of pond water are as follows :
Optimum basic parameters of water
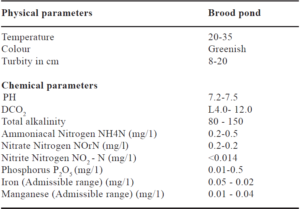
Oxygen stress
Sometime the brood pond develop bloom, resulting drop down of dissolve oxygen below 4 ppm which gives physiological stress to brood. In such events certai measures like reduction of feeding rate and aeration of pond helps to overcome th situation.
Physical stress
The carps are found to breed at a fairly wide range of pH and dissolved oxygen But many fishes do not breed in water which is poor in oxygen content. Renewal of water induces them to breed.
Summary
Fish seed is the most important component for fish culture.
The fish seed is obtained from three sources – riverine, hatcheries and bundhs. The collection of seed from riverine source was an age old practice. This method is strenuous and we get the mixture of wanted and unwanted fish seed. Hatcheries are the best way of getting fish seed. Apart from these, the bundh breeding is also a good method to collect the fish seed by creating a natural habitat.
Carps breed in flowing waters like rivers.
In induced breeding techniques, four main types of materials are used to give injections to fish – pituitary gland extractions, HCG, ovaprim and ovatide.
Fish breeding by pituitary gland extraction is an effective and dependable way of obtaining pure seed of cultivable fishes and is practiced today on a fairly extensive scale in India as well as many other countries in the world. It involves injecting mature female and male fishes with extracts of pituitary glands taken from other mature fish.
Fish pituitary gland is a small, soft body and creamish white in colour. It is more or less round in carps. It lies on the ventral side of the brain Pituitary gland secretes the gonadotropic hormones, FSH or Follicular Stimulating Hormone, and LH or Luteinizing Hormone. Both hormones are secreted through out the year, but the proportion in which they are secreted is directly correlated with the cycle of gonadal maturity. The FSH causes the growth and maturation of ovarian follicles in females and spermatogenesis in the testes of males. LH helps in transforming the ovarian follicles into corpus lutea in females and promoting the production of testosterone in males.
The pituitary glands can be preserved by three methods – absolute alcohol, acetone and freezing. Preservation of fish pituitary gland in absolute alcohol is preferred in India.
H.C.G. is human chorianic Gonadotropin is produced by placenta in pregnent ladies. During early stages of pregnancy H.C.G. is rich in the urine of pregnant women.
Ovaprim is a ready to use product and the solution is stable at ambient temperature. It contains an analogue of 20 µg of Salmon gonadotropin releasing hormone (sGnPHa) and a dopamine antagonsist, domperidone at 10 mg/ml. The potency of ovaprim is uniform and contains sGnRHa which is known to be 17 times more potent than LH-RH (Peter, 1987). The dopamine antagonist, domperidone used in ovaprim is also reported to be better than another commonly used antogonist, pimozide. Ovaprim being a ready to use product and one which does not require refrigerated storage, appears to be the most convenient and effective ovulating agent.
Ovatide is an indigenous, cost-effective and new hormonal formulation for induced breeding of fishes. The new formulation is having the base of a synthetic peptide which is structurally related to the naturally occuring hormone, goanadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH). GnRH is not a steroidal hormone and belongs to the class of organic substances called peptides.
Ovopel, developed by the University of Godollo in Hungary, is a preparation containing mammalian GnRH and the water-soluble dopamine receptor antagonist, metoclopramide. The concentration of D-Ala6, Pro9NEt-mGnRH and metoclopramide are in the form of 18-20 micro gm/pellets and 8-10mg/pellets respectively.
Other substances like LH-RH analogues, steroids, and clomiphene are used for induced breeding of fishes.
Environmental factors like temperature, water condition, light, meteorological . conditions, etc. are important factors controlling the reproduction of fish.
Many types of hatcheries have been established so far for hatching fish eggs. The main aim of the hatcheries is to improve the percentage of the hatching of eggs.
Transportation of breeders, fry and fingerling is a common phenomenon in fish culture systems. The fish seed are transported from hatchery units to the fish farm to rear them in culture systems. The breeders are usually transported from culture system to hatchery units for breeding either by induced breeding or naturally.
Several types of containers are used in the transport of fish seed. These are mud pots, round tin carriers, double tin carriers, oxygen tin carriers and tanks fitted on lorries. The containers are transported by bicycles, carts, rickshaws, boats, lorries, trains and aeroplanes.
Recent investigations have shown that the fish seed could be anesthetised for transportation for ensuring better survival rate. The purpose of this is to ensure that the fish seed survives for a longer period of time, and also to minimise the concentration of toxic gases like ammonia and carbon dioxide in the medium by lowering the metabolic rate of the fish seed. Anesthetised fish seed have been found to survive for double the time of unanesthetised seed, besides ensuring a better survival rate, which is about 90%. Carbonic acid has been found to be the best anesthetic compared to others such as quinaldine, sodium amytal, urathane, veronal chloroabutanal and TMS-222 (Tricaine Methan Sulphonate). Carbonic acid is not only cheap but also safe and easy to use.
Hence, Adequate prime brood are essential for commercial seed production. Brood management practices deals mainly with the brood recruitment, pond management and stress management.
Source: Aquaculture
