

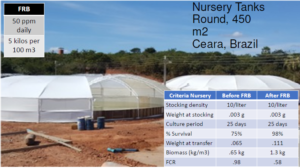
• Before FRB: 60-75% survival
• After FRB: 80-90% survival
• Juveniles grew faster (2-5 days)
• Increased survival in grow-out ponds
• 50 ppm FRB daily (5 kilos per RW)
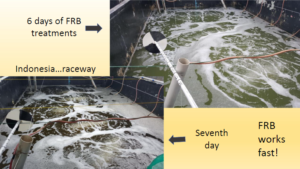
Synbiotics and recirculation for extensive grow-out systems
Survival using FRB only: 40-60%
Survival using FRB + recirculation: 60-80%
Recirculation model: Within grow-out ponds
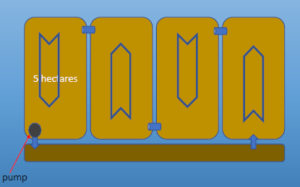
Harvest: 2,500-5,000 kilos per hectare
Survival: 75-85%; 150 days; 30-33 grams
• Series of 2-5 ponds
• Up to 7 hectare ponds
• Ecuador and Mexico
• Zero aeration; static ponds
• Daily exchange: 1% (before 10%)
• One pump; gravity flow
• Stocking density: 20-30/m2
Water movement helps to optimize synbiotics in extensive ponds
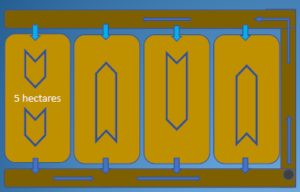
Recirculation in parallel
• Farm level or groups of ponds
• Staggered stocking
• Longer period to balance water quality
• Large pump and energy costs
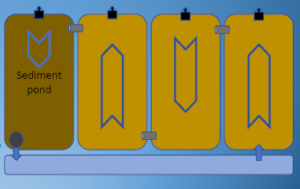
Recirculation in series
• 2-6 ponds
• Batch stocking
• 2 grams – recycle
• Free board: 5 cm
Shrimp Farm in Mexico
Before: Open exchange of 10% pond volume per day for entire farm; 80% mortality due to EMS
Plan for 2018:
• synbiotics and recirculation
• 1% open exchange per day
• 12 hours of recirculation per day (night)
FRB without aeration
• Mix FRB 2-3 times per day
• 24 hours of anaerobic fermentation
• 15 kilos of rice bran / hectare / week
• Applied every 2-3 days



• Mineralize pond bottom w/enzymes & FRB
• Before and after stocking
• Breaks up biofilm, enhances diatoms
• 1-2 times per week (rope for lined ponds)
Amino Peptide (AP) Emulsion
• Protein (from soy) converts to amino acids and peptides
• 5 to 7 day anaerobic fermentation (stir daily)
• 10-20% AP emulsion on one feeding per day
Application
Top coat for feed – 100-200 ml per kilo
Fermentation period of feed – 1 to 12 hours before feeding
Feed treatments – One feeding per day
Direct pond treatment – 2 ppm/hectare; twice weekly

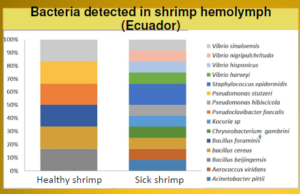
Bacteria detected in shrimp hemolymph (Ecuador)
Amino Peptide(AP) Emulsion Protocol
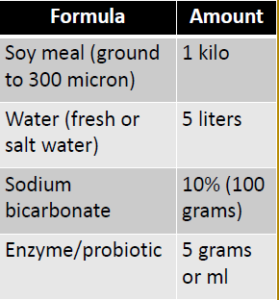
• Top coat for feed: 100-200 ml per kilo of feed
• Treat one feeding per day
• Direct pond treatment: 2 ppm per hectare twice per week
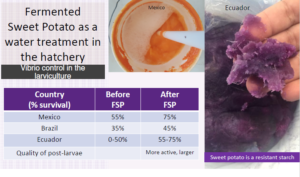
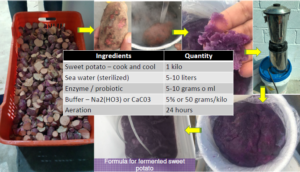
Fermented Sweet Potato as a water treatment in the hatchery

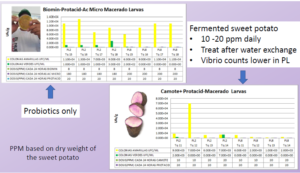


Comparing biofloc, high exchange and synbiotics
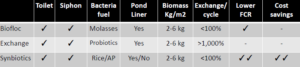
1.Biofloc – difficult to manage organic load
2.High exchange – water storage, high energy, discharge, higher FCR
3.Synbiotics – low organic load, water exchange, FCR, easy to manage
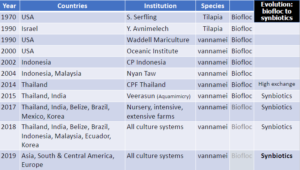

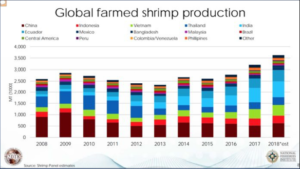
Synbiotics is a long-term and sustainable solution Back to the future…
Source: Society of Aquaculture Professionals (SAP)
